Aadhar Enabled Payment System| SprintOPN
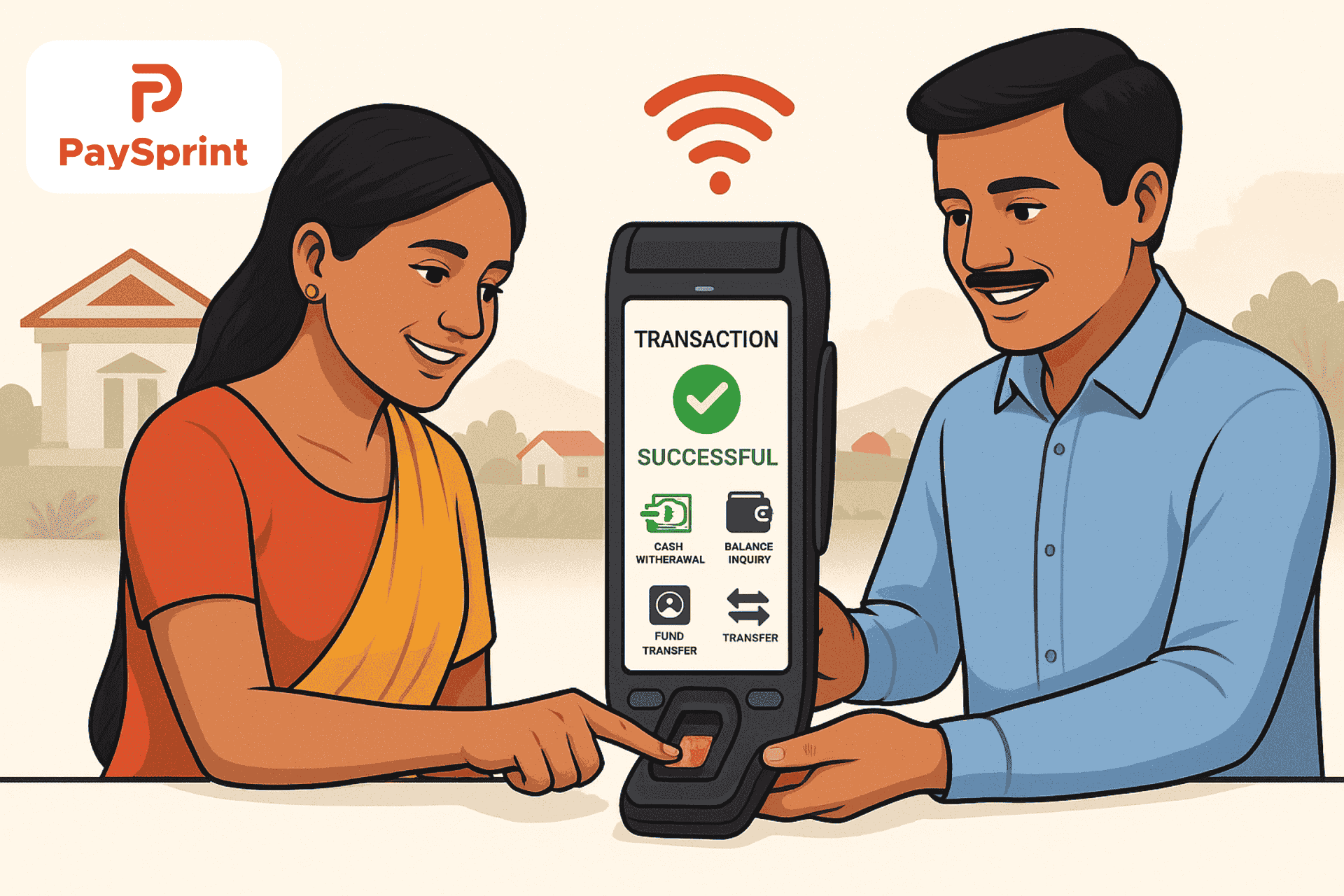
The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS) is a payment service that enables a bank user to access their Aadhaar-enabled bank account and carry out standard banking operations, such as checking their balance, withdrawing cash, and sending money through a business correspondent, using their Aadhaar as identification.
What is AEPS?
AEPS is a bank-driven framework that facilitates online
interoperable financial transactions at Points of Sale (PoS) or Micro ATMs
through any banking institution's Business Correspondent (BC) or Bank Mitra,
utilizing Aadhaar authentication.
Table of Content
1.
How Does APES Work?
2.
Features of AEPS
3.
Benefits of AEPS
4.
Types of APES
5.
How to use AEPS
6.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AEPS
7.
Service Offered by AEPS
8.
Objective of AEPS
9.
Future of AEPS
How does AEPS Work?
Step 1- Visit a micro-ATM or banking
correspondent.
Step 2- Enter the number from your
Aadhaar.
Step 3- Select the type of
transaction.
Step 4- Put the sum in.
Step 5- Give your biometric
information (iris scan or fingerprint).
Step 6 - Verify the transaction.
Step 7- Get your money back or get a
confirmation message.
Features of AEPS?
1.
Aadhar-based authentication: Using
the Aadhaar number, AEPS facilitates transactions while ensuring security
through biometric authentication (fingerprint or iris scan).
2.
Interoperability:
Regardless of the bank a user is registered with, AEPS enables them to conduct
transactions across many banks and financial organizations.
3.
Basic Transaction: The
system facilitates the following simple banking transactions:
1. Cash
Withdrawal: Customers have the option to take money out of their
accounts.
2. Balance
Inquiry: Customers can view the amount in their accounts.
3. Mini
Statement: A summary of recent transactions is available
to users.
4. Funds
transfer: Moving funds between bank accounts is known as a fund
transfer.
4.
Offline Transaction: AEPS
can operate with a basic biometric-based system in places with poor internet
connectivity.
5.
Security: The
system offers a high degree of protection for user transactions, lowering the
danger of fraud, because it depends on biometric data (fingerprint or iris).
6.
Financial Inclusion: For
those living in rural or isolated locations who might not have access to
smartphones or traditional banking infrastructure, AEPS offers banking
services.
7.
Fast and Simple Access: AEPS
enables consumers to conduct financial transactions with as little
infrastructure as possible, such as a biometric-scan-capable point-of-sale
(POS) terminal.
8.
Cost-effective: It
provides a reasonably priced banking and financial transaction solution,
particularly in isolated locations where traditional banking options may be
limited.
9.
24/7 Availability: AEPS
offers 24/7 banking services and is accessible anytime.
Benefits of AEPS
For every group in society, the Aadhaar-enabled payment
system (AePS) provides several advantages:
1.
Ease of Use: People
may easily do a variety of financial transactions with AePS because it is made
to be straightforward to use.
2.
Biometric Security: To
guarantee safe and reliable transactions, the system combines the Aadhaar
number with biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or iris scans.
3.
Empowering the Underprivileged: By
facilitating digital financial transactions and giving impoverished communities
access to basic banking services, AePS promotes financial inclusion.
4.
Bank Information Privacy: By
enabling transactions without revealing bank account information, users'
security and privacy are improved.
5.
Convenient Bank Access: By
using Aadhaar authentication, users may quickly access their bank accounts,
negating the need for in-person bank visits.
Types of AEPS
1.
Aadhar Pay: Uses a
customer's Aadhaar number to enable shops to transfer funds to any bank
account.
2.
Balance Enquiry: Enables
customers to use their Aadhaar number to check the balance of their bank
accounts.
3.
Paytm AEPS: This
service, which is a component of the Paytm digital payment platform, enables
users to conduct financial transactions by utilizing their Aadhaar number.
4.
BHIM Aadhar Pay:
Using their Aadhaar number and biometric authentication, customers can pay
participating merchants with this merchant payment service.
How to use AEPS For transaction?
The following describes the steps that must be taken to use
AEPS:
Step 1: Visit a banking correspondent
or micro ATM.
Step 2: Enter the bank name and
Aadhaar number.
Step 3: Select the transaction type
and what kind of transaction you wish to do.
Step 4: Enter the transaction amount
to proceed with the transaction.
Step 5: Use a fingerprint scan to
confirm the transaction.
Step 6: Get your invoice.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of AEPS
|
Features |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Convenient
to use |
Eliminates
the need for debit cards and PINs by streamlining access through the use of
Aadhaar and fingerprint. |
dependent
on internet and fingerprint scanner technologies, which can be unreliable in
places with inadequate connectivity. |
|
Easy to
Access |
Uses
nearby stores with micro ATMs to make banking easier in places far from
banks. |
AEPS
services are not well known or accessible, especially in places with poorer
internet connections. |
|
Transaction
Type
|
Meets
basic financial needs by offering banking services including deposits and
cash withdrawals. |
Its
usefulness for more complex financial needs, such as loans, is limited
because it does not enable complex banking transactions. |
|
Fraud
and Risk |
AEPS
is normally safe, but if security measures are inadequate, there is a chance
of fraud. |
In
places where security procedures are not rigorously followed, fraud risks may
rise. |
|
Security |
By
guaranteeing that only the account holder may access their account, biometric
authentication can improve security. |
raises
further privacy issues regarding the security and use of biometric data. |
|
Inclusion
Requirement |
Improves
financial inclusion by reaching underserved populations in remote
locations |
Access
is restricted to those who have an Aadhaar number; anyone without this
identity cannot enter. |
Serviced offered by AEPS
The other services offered by the AEPS are as follows:
1.
eKYC
2.
Tokenization
3.
Aadhaar seeding status
4.
Authentication
AePS's goals
1.
Encourage Financial Inclusion: Give
those living in rural and underserved areas access to banking and financial
services.
2.
Encourage the Digital India Project:
Reduce the amount of cash used and streamline digital transactions.
3.
Simplify Transactions: Make
both financial and non-financial transactions simple by offering an
Aadhaar-based payment mechanism.
4.
Promote Cashless Economy: To
support the government's goal of a cashless economy, promote digital payments.
5.
Interoperability Across Banks: Use
Aadhaar verification to facilitate easy transactions across several banks.
Transaction Limit for AEPS
A daily cap of Rs. 50,000 on the total number of
transactions has been imposed by certain banks. The NPCI has set a maximum
withdrawal limit of Rs. 10,000 per AEPS transaction.
What does the AEPS's future hold?
To enhance financial transactions, the Indian government
and the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) launched the Aadhaar
Enabled Payment System (AEPS). For this, they intended to employ an Aadhaar
card. This payment method is groundbreaking. This payment method was made
by the creators. In these rural locations, they hope to provide improved
employment opportunities. Access to banking facilities is restricted in
certain regions. As more Indians become aware of the advantages of AEPS, its
future seems quite promising. Several Indian banks have already implemented
AEPS.
Conclusion: AEPS
In India, the Aadhaar Enabled Payment System
(AePS) is a revolutionary digital payment system that has
contributed to the increased accessibility and security of banking services. It
is anticipated to keep developing and be crucial to India's financial future.
FAQs- AEPS
Q1. What is Aeps and how it works?
AEPS is a bank-driven framework that facilitates online
interoperable financial transactions at Points of Sale (PoS) or Micro ATMs
through any banking institution's Business Correspondent (BC) or Bank Mitra,
utilizing Aadhaar authentication for verification.
Q2. Are AEPS and UPI the same?
AEPS and UPI serve different purposes. AEPS operates by
utilizing Aadhaar and biometric authentication for transactions, specifically
targeting rural and underbanked populations.
In contrast, UPI (Unified Payments Interface) facilitates
instantaneous payments through mobile numbers or UPI IDs, emphasizing digital
transactions
Q3. Is AEPS safe to use?
AEPS, or Aadhaar Enabled Payment System, is a secure
payment solution offered by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
It enables individuals with bank accounts linked to their Aadhaar numbers to
conduct financial transactions effortlessly through Aadhaar-based
authentication.
Q4. What is the limit of AEPS per day?
The daily transaction limit for the Aadhaar Enabled Payment
System (AEPS) is determined by individual banks and the specific nature of the
transaction. The highest permissible cash withdrawal amount through AEPS is Rs
10,000 for each transaction.
Q5. Who Controls AEPS?
The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS) is a
banking-oriented framework established by the National Payments Corporation of
India (NPCI).
Q6. What is the age limit for AEPS?
As per the guidelines issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), there is no specific age limit for using AEPS.




