Micro ATM vs Traditional ATM: Which Banking Model Fits India’s Future?
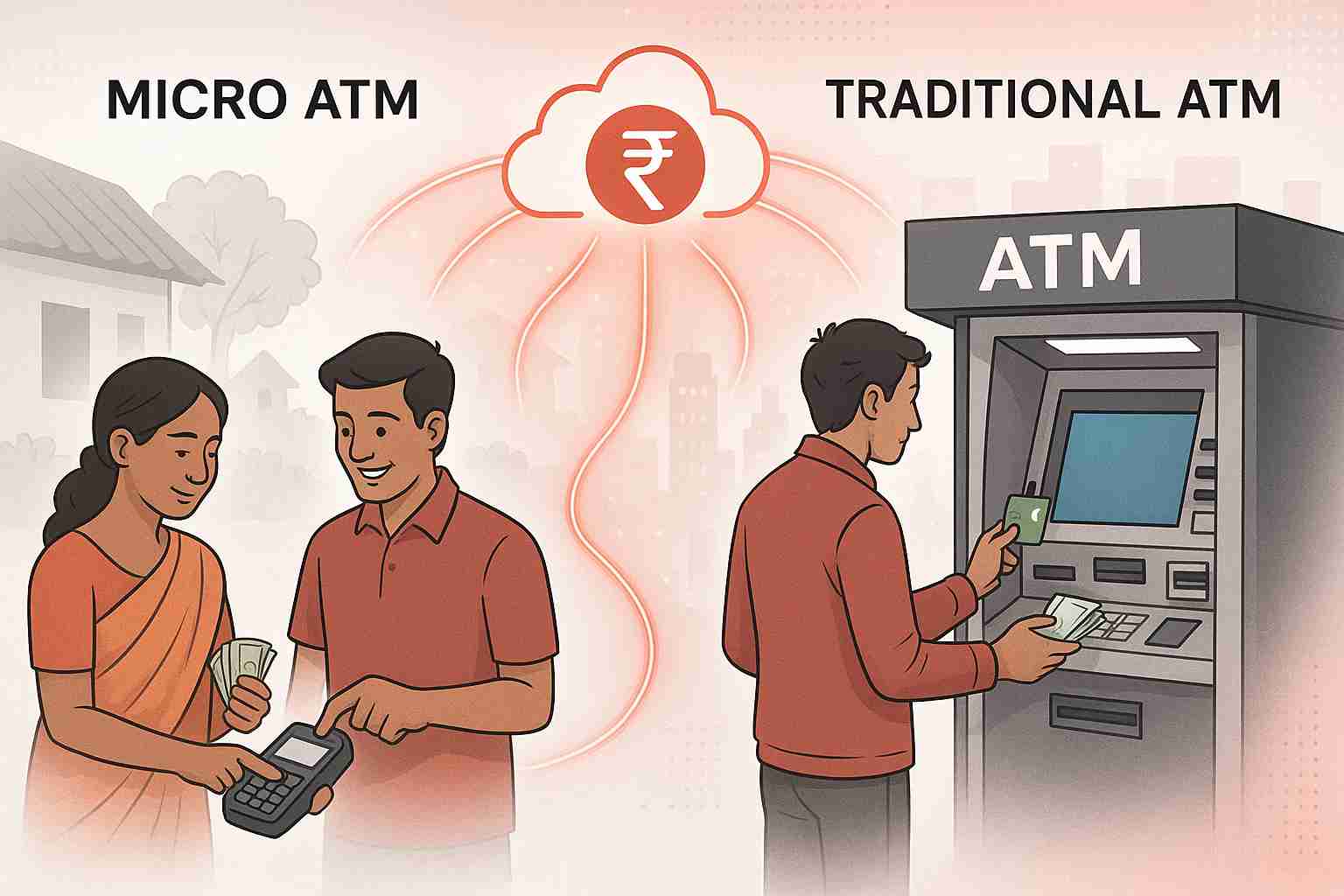
Banking in India is undergoing a major transformation. While traditional ATMs have long been the backbone of cash withdrawals and basic banking, Micro ATMs are rapidly emerging as a smarter, more accessible solution for last-mile banking. Especially in rural and underserved regions, Micro ATMs are helping bridge the financial inclusion gap. But how do they compare to traditional ATMs in terms of accessibility, cost, features, and infrastructure?
Table of Contents
1.
What
is a Micro ATM?
2.
What
is a Traditional ATM?
3.
Key
Differences Between Micro ATM and Traditional ATM
4.
Why
Micro ATMs are a Game Changer for Rural India
5.
Advantages
of Traditional ATMs
6.
Cost
and Scalability: A Business Perspective
7.
Which
is the Right Model for India’s Future?
8. Conclusion
What is a Micro ATM?
A Micro ATM is a handheld device that enables basic banking services like cash withdrawal, balance inquiry, and fund transfer. These devices are typically operated by banking correspondents (BCs) or agents and are powered by Aadhaar-enabled Payment Systems (AEPS) or debit cards. They are designed to bring banking to the doorstep of users in rural, remote, and semi-urban areas where conventional ATMs may not be viable. To learn more about how Micro ATMs are shaping financial inclusion in India, read this detailed blog: What is a Micro ATM & How Does It Work?
What is a Traditional ATM?
A Traditional
ATM (Automated Teller Machine) is a large, fixed machine usually found in
urban and suburban centers. It provides users with access to their bank
accounts to perform operations such as withdrawing cash, checking balances, and
printing mini-statements.
While widely used, traditional ATMs are infrastructure-heavy, costly to maintain, and often inaccessible in rural pockets.
Key Differences Between Micro ATM and Traditional ATM
While both
Micro ATMs and traditional ATMs serve the purpose of enabling access to banking
services, their operation, infrastructure, and usability vary significantly.
Here's a breakdown of the major differences:
1.
Infrastructure:
Micro ATMs
are compact, portable, handheld devices that can be easily carried and operated
by banking agents or shopkeepers. In contrast, traditional ATMs are large,
fixed machines installed in booths or kiosks, requiring more space and a permanent setup.
2.
Deployment Cost:
The cost of
setting up a Micro ATM is considerably lower than a traditional ATM. Micro ATMs
need minimal infrastructure and power, whereas traditional ATMs involve higher
installation, maintenance, and security expenses.
3.
Operation Model:
Micro ATMs
are operated by a banking correspondent or authorized agent who facilitates
transactions for the user. On the other hand, traditional ATMs are self-service
machines where customers independently perform their transactions.
4.
Connectivity:
Micro ATMs
typically use mobile data or low-bandwidth internet connections, making them
suitable for remote and low-connectivity regions. Traditional ATMs rely on
wired internet connections or leased lines, which are more suitable for urban
environments with reliable infrastructure.
5.
Services Offered:
Micro ATMs
offer basic banking functions such as cash withdrawal, balance inquiry, and
fund transfer using Aadhaar or debit card authentication. Traditional ATMs
generally provide a broader range of services, including cash deposits,
mini-statements, PIN changes, and fund transfers between accounts.
6.
Location Suitability:
Micro ATMs
are ideal for rural and semi-urban locations due to their portability
and minimal power requirement. Traditional ATMs are more suitable for urban
and suburban areas where infrastructure support like electricity, internet,
and security is readily available.
7.
Power Requirement:
Micro ATMs
consume very little power and can run on batteries or low-power connections,
which is critical for deployment in areas with irregular electricity supply.
Traditional ATMs, however, require a continuous electric supply and often need a
power backup system, increasing operational costs.
These differences make it clear that Micro ATMs are purpose-built for expanding financial access to underserved areas, whereas traditional ATMs cater better to high-volume, infrastructure-rich environments.
Why Micro ATMs are a Game Changer for Rural India
Micro ATMs are particularly effective in areas where bank branches and ATMs are few. With minimal setup and operational costs, banks can extend their reach without the logistical and financial burden of setting up full ATMs. Their biometric and Aadhaar-based authentication also ensures secure transactions for users with limited digital literacy.
Advantages of Traditional ATMs
While traditional ATMs are costlier to maintain, they offer a broader range of services and higher daily withdrawal limits. They are best suited for urban customers with access to power, internet, and banking infrastructure. Many now offer multi-bank transactions, cheque deposit features, and multi-language support.
Cost and Scalability: A Business Perspective
Micro ATMs offer a cost-effective and scalable model. For banks and fintech companies, investing in Micro ATMs allows wider geographic coverage with faster ROI. Traditional ATMs, though robust, demand ongoing costs for maintenance, power backup, security, and space rental.
Which is the Right Model for India’s Future?
India’s path to financial inclusion requires innovative, scalable, and accessible banking models. While traditional ATMs will remain relevant in metros and tier-1 cities, Micro ATMs are poised to dominate rural and tier-3 markets, thanks to their affordability, portability, and simplicity.
Conclusion
The rise of Micro ATMs reflects India’s push toward a cash-lite, inclusive banking ecosystem. Their ability to reach remote corners of the country without the need for heavy infrastructure makes them a strategic tool for banks, NBFCs, and fintech firms. Platforms like the Micro ATM API empower businesses to deploy and manage Micro ATMs efficiently, helping extend banking services across diverse geographies. While both Micro and traditional ATMs have unique roles in the banking ecosystem, together, they support a hybrid model that meets the varied needs of both urban and rural India.
FAQs
What is the main benefit of Micro ATMs?
Micro ATMs
offer low-cost, portable banking solutions ideal for rural and remote areas
without bank branches or traditional ATMs.
Are Micro ATMs secure?
Yes, Micro
ATMs use biometric authentication via Aadhaar and PIN verification to ensure
secure transactions.
Can I deposit cash using a Micro ATM?
Currently,
most Micro ATMs support only withdrawal and balance inquiries, but newer models
may support deposits depending on the service provider.
Who can operate a Micro ATM?
Banking
correspondents, local shopkeepers, or business owners can operate Micro ATMs
after authorization by banks or fintech companies.
Which is more cost-effective: Micro ATM or Traditional ATM?
Micro ATMs
are far more cost-effective to deploy and maintain compared to traditional
ATMs, especially in low-footfall areas.