API Banking: Types and How It Works?
Application Programming Interface (API) Banking: API
Banking uses XML/JSON codes (APIs) to communicate between the bank and client
servers, facilitating data transfer between these two systems and guaranteeing
a secure and smooth integration between the bank and the customer's systems.
This feature enables the customer to conduct banking
transactions easily without switching between the bank and the Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP) platform.
Table of Contents
1.
What is API Banking?
2.
Types of Banking APIs
3.
How API Banking Works?
4.
Benefits of API Banking
5.
Simplifying Financial Services with APIs
6.
Future Impact and Monetization Potential
7.
Conclusion
API Banking
API Banking enables secure, real-time communication between
a bank’s core system and third-party platforms through APIs (Application
Programming Interfaces), typically built using XML or JSON. This allows
businesses to access banking services—like payments, account data, and
loans—without switching between systems, such as an ERP or mobile app.
Types of Banking APIs
1.
Open Banking APIs
Enable secure sharing of customer data with authorized third-party providers,
offering users access to a broader range of financial services while retaining
control over their data.
2.
Payment APIs
Facilitate seamless financial transactions like money transfers, bill payments,
and purchases within digital platforms.
3.
Data APIs
Provide access to essential financial information such as balances, transaction
histories, and statements, aiding in analytics and decision-making.
4.
Authentication APIs
Ensure user identity verification through secure methods like two-factor
authentication or biometrics, protecting access to financial services.
5.
Lending APIs
Streamline the loan lifecycle—from application to approval and
disbursement—enabling faster and more efficient access to credit.
6.
Core Banking APIs
Connect external systems to a bank’s central infrastructure, enabling functions
like account management, transaction processing, and customer services.
7.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) APIs
Allow
non-banks to offer financial services by leveraging the infrastructure of
licensed banks, such as digital accounts or payment solutions.
8.
Fraud Detection APIs
Use advanced analytics to monitor transactions for suspicious activity,
enhancing security and minimizing financial risk.
9.
Regulatory & Compliance APIs
Help
financial institutions meet legal requirements by automating KYC, AML, and
other compliance processes.
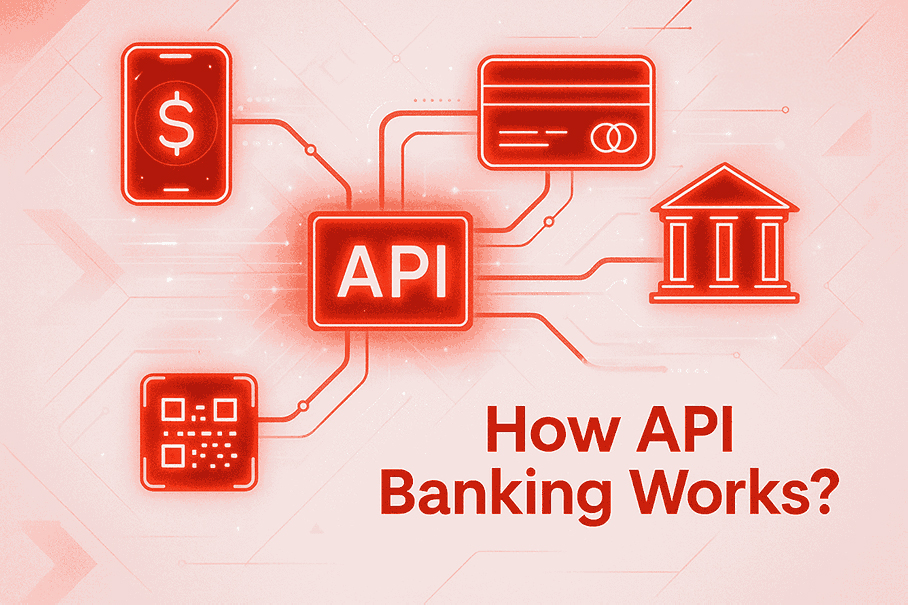
How Does API Banking Work?
1.
Customer Makes a Request
A user initiates a transaction via a fintech app or e-commerce site.
2.
App Sends API Call
The app connects with the bank via a public API
3.
Bank Receives Request
The API forwards transaction details securely to the bank's core system.
4.
Verification and Processing
The bank authenticates the user, checks the balance, and runs fraud checks.
5.
Transaction Completion
The bank executes the transaction and updates records.
6.
Response Sent to App
The customer receives confirmation in real-time.
Benefits of API Banking
1.
Faster Transactions: Enables
real-time processing with minimal friction.
2.
Improved Customer Experience: Users
can manage finances within one interface.
3.
Secure and Compliant: Modern
APIs follow REST/OpenAPI standards with built-in security.
4.
Automation & Efficiency: Reduces
manual work through system integration.
5.
Data Accessibility: Breaks
data silos and unlocks business insights.
6.
Scalability: Easily
integrate or upgrade modules without system-wide changes.
7.
Product Innovation: Banks
can collaborate with fintechs to create new offerings.
How APIs Simplify Financial Services
API banking supports modular
system design, allowing banks to:
1.
Update components without disrupting the entire
system.
2.
Integrate new third-party tools like Plaid or
Yodlee effortlessly.
3.
Deploy updates incrementally and test
efficiently.
4.
Maintain service stability even during
upgrades.
The Future and Monetization Potential of API Banking
API banking is central to the digital transformation of the financial sector. It enables banks to generate new revenue streams by offering APIs as commercial products, while also allowing fintechs to build innovative services on top of existing banking infrastructure. Internally, APIs streamline operations through automation, reduce costs, and support faster innovation. As API adoption grows, banks become more agile, competitive, and better equipped to meet evolving customer expectations.Conclusion: Why API Banking Matters
API Banking is revolutionizing how financial services are
delivered. It empowers banks and fintechs to collaborate, enhance customer
experiences, and innovate at scale. As open banking and embedded finance grow,
API Banking will remain central to building a modern, interconnected financial
ecosystem.